Cybersecurity is the body of technologies, processes, and practices designed to protect networks, computers, programs and data from attack, damage or unauthorized access. As we enter in 2017, we become more and more dependent on technology, cyber security threats may only increase, and here we look at 4 of the biggest cyber security threats.
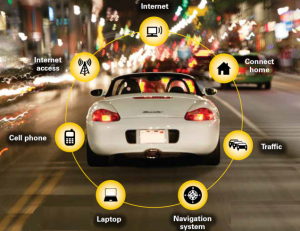
1- Connected cars
A connected car is a car that is basically connected to the internet. It is usually defined as a car able to optimize its own operation and maintenance as well as the convenience and comfort of passengers using sensors and internet connectivity. This is typically done through embedded, tethered or smartphone integration. These types of cars are becoming more and more popular amongst people, as they account for half of the vehicles sold in 2015. A study also claims that all cars sold by 2025 will be connected. With these types of cars, there come obvious and serious threats. Hackers might try to enter the system by manipulating vulnerabilities in insecure systems, and steal important and valuable data. Not only this, but the hackers might enter the system, and might as well control the brakes, steering, and transmission, all this from a laptop far away. Another threat might be posed by the fact that very sensitive data might be stolen from your car, for instance where you went the night before, your daily routes, and maybe even your conversation over Bluetooth connectivity. Hackers can be very creative, so using these types of cars can be very dangerous.
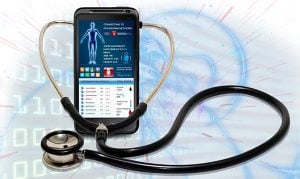
2- Smart Medical Devices and Electronic Medical Records (EMRs)
Like many industries going through digitalization, the healthcare industry isn’t far off from the digitalization of its own. With this digitalization, patient records are going online, and obviously, threats are also posed as this digitalization process is gaining pace in the healthcare industry. As the healthcare industry becomes connected to the internet, more and more patient data has become vulnerable, with the threat that hackers might want to steal valuable medical records or related data. Even more dangerous is the fact that some devices might be connected straight to the patient. The hacker may try and succeed in increasing or decreasing the amounts of dosages given to a patient, or the hacker might even disable crucial monitoring.
3- Third Parties (Vendors, Contractors, Partners)
Third parties may include vendors and contractors, and most of these pose a huge threat for cooperations that don’t have the right people or a team in place to help protect against these third party employees. As the problem of the cyber threat increases, the organization is becoming more and more aware of the threats these third parties pose. In 2015, Wendy’s fell victim to a data breach that affected at least 1,025 of the fast-food chain’s locations and was caused by a third-party vendor that had been hacked. Similarly, hackers stole the data of 110 million Target customers in 2013 by exposing a vulnerability in the retailer’s third-party refrigeration vendor. In 2017, these third party attacks and threats are only likely to increase, hence it is very important for organizations to protect themselves against such threats.

4- Cyber Espionage
Hackers now are becoming more and more creative, and they are not only hacking into companies data, and making a profit by stealing sensitive data, but now hackers in groups are threatening government infrastructure by hacking. So basically, hacking now is not only done on a private scale, but also to a government level. Such is the case for the threats that President Obama’s 2017 fiscal year budget proposes a $19 billion allocation toward cyber security. These threats can be very dangerous for the country attacked, as very sensitive and private information like weapons and contracts might be obtained, which might, in turn, increase terrorism.

The major problem concerning cyber crimes is that not many professionals know how to properly protect against such threats, and this is the reason that the University of San Diego has created two master’s degree programs focused specifically on the major issues facing cybersecurity professionals today.




